Primary : dbadeeds
Standby : rdbadeeds
- nstall Latest EDB Postgres version on the database server using yum install
- On Primary: Configure the Postgres DATA folder & WAL folder
- On standby: Just install EDB Software itself
- Validate the primary database server:
- Step 1: Configuring the PostgreSQL Master/Primary Database Server
- On the master server, switch to the postgres system account and configure the IP address(es) on which the master server will listen to for connections from clients. In this case, we will use *meaning all.
- # su – enterprisedb
$ psql -c “ALTER SYSTEM SET listen_addresses TO ‘*’;
- # su – enterprisedb
- Then create a replication role that will be used for connections from the standby server to the master server, using the createuser program. In the following command, the -P flag prompts for a password for the new role and -e echoes the commands that createuser generates and sends to the database server.
- # su – enterprisedb
$ createuser –replication -P -e replicator
$ exit
- # su – enterprisedb
- Then enter the following entry at the end of the /pgdata/epas13/pg_hba.conf client authentication configuration file with the database field set to replication as shown in the screenshot.
- host replication replicator 146.*.*.*/24 md5
- Now restart the Postgres13 service using the following systemctl command to apply the changes.
- # systemctl restart edb-as-13
- Step 2: Making a Base Backup to Bootstrap the Standby Server
- On Standup Server
- systemctl stop edb-as-13
# su – enterprisedb
$ cp -R /pgdata/epas13/ /pgdata/epas13/data_orig
$ rm -rf /pgdata/epas13/* - Then use the pg_basebackup tool to take the base backup with the right ownership (the database system user i.e Postgres, within the Postgres user account) and with the right permissions.
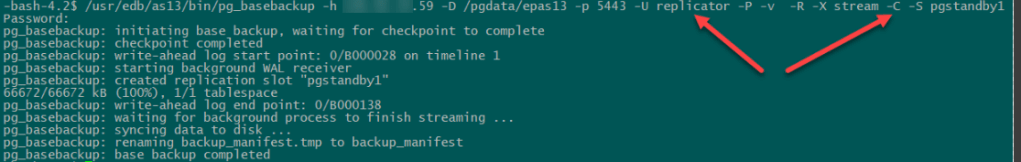
- When the backup process is done, the new data directory on the standby server should look like that in the screenshot. A standby.signal is created and the connection settings are appended to postgresql.auto.conf. A replication slave will run in “Hot Standby” mode if the hot_standby parameter is set to on (the default value) in postgresql.conf and there is a standby.signal file present in the data directory.
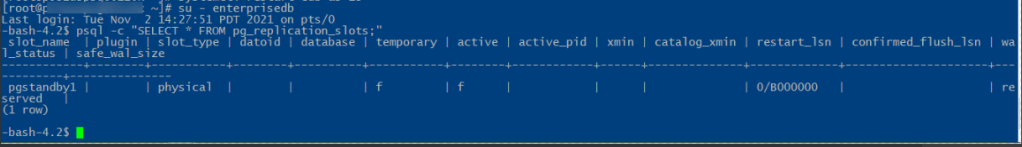
- Now back on the master server, you should be able to see the replication slot called pgstandby1 when you open the pg_replication_slots view as follows.
- # su – enterprisedb
$ psql -c “SELECT * FROM pg_replication_slots;”
- # su – enterprisedb
To view the connection settings appended in the postgresql.auto.conf file,Now commence normal database operations on the standby server by starting the PostgreSQL service as follows.
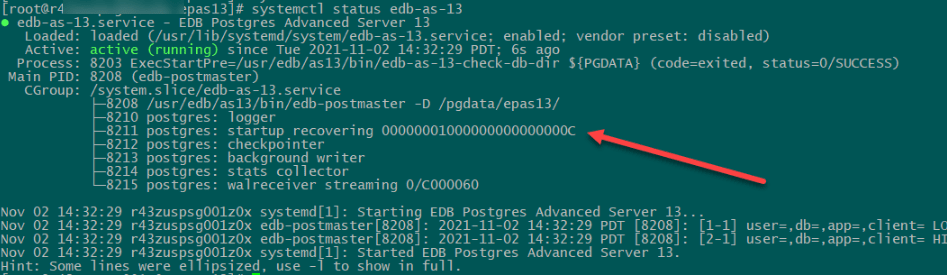
Step 3: Testing PostgreSQL Streaming Replication
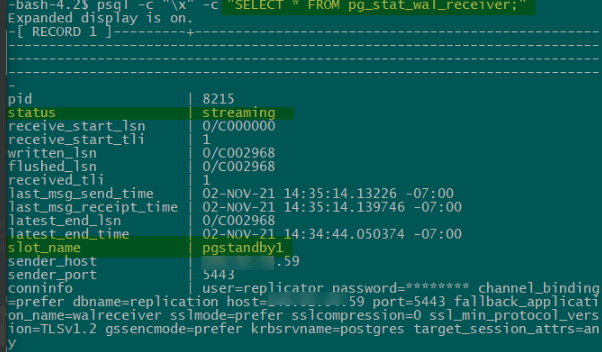
- Once a connection is established successfully between the master and the standby, you will see a WAL receiver process in the standby server with a status of streaming, you can check this using the pg_stat_wal_receiver view.
- $ psql -c “\x” -c “SELECT * FROM pg_stat_wal_receiver;”
- On Standby
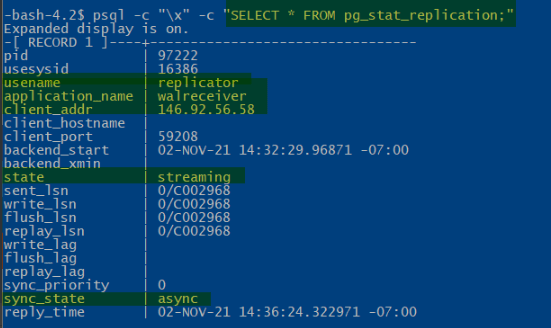
On Primary : Corresponding WAL sender process in the master/primary server with a state of streaming and a sync_state of async, you can check this pg_stat_replication pg_stat_replication view.
- $ psql -c “\x” -c “SELECT * FROM pg_stat_replication;”
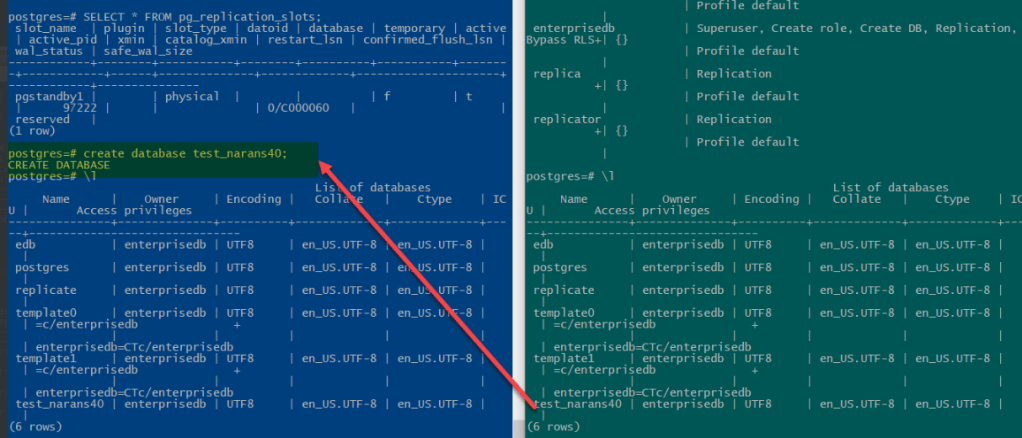
Create Database creation on primary server
Leave a comment